Initialization of an ArrayList in one line
Categories:
Initializing an ArrayList in a Single Line in Java

Explore various concise methods for initializing Java ArrayLists, from classic approaches to modern Java 8+ streams, enhancing code readability and efficiency.
Initializing an ArrayList and populating it with initial values is a common task in Java programming. While there are traditional multi-line approaches, modern Java offers several concise, single-line (or near single-line) methods to achieve this. This article will delve into these techniques, discussing their advantages, disadvantages, and appropriate use cases, helping you write cleaner and more efficient code.
The Classic Double Brace Initialization (Avoid)
One of the oldest and most frequently cited methods for initializing an ArrayList in a single statement is the 'double brace initialization'. This technique uses an anonymous inner class to create and populate the list. While it appears concise, it has significant drawbacks that make it generally discouraged in modern Java development.
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>() {{
add("Apple");
add("Banana");
add("Cherry");
}};
Example of double brace initialization
Using Arrays.asList() (Fixed-Size List)
The Arrays.asList() method provides a simple way to create a List from an array of elements. While it's concise, it's crucial to understand that the List returned by Arrays.asList() is a fixed-size list backed by the original array. This means you cannot add or remove elements from it. If you need a mutable ArrayList, you must wrap the result in a new ArrayList constructor.
// Fixed-size list (cannot add/remove elements)
List<String> fixedList = Arrays.asList("Red", "Green", "Blue");
// Mutable ArrayList
ArrayList<String> mutableList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("Alpha", "Beta", "Gamma"));
Initializing with Arrays.asList()
Arrays.asList() when you need a quick, immutable list for iteration or passing to methods that accept Collection or List interfaces, and you don't intend to modify its size.Java 9+ List.of() (Immutable List)
Introduced in Java 9, List.of() offers the most concise and efficient way to create an immutable list with initial elements. This method is highly recommended when you need a list whose contents will not change after creation. Attempting to modify a list created with List.of() will result in an UnsupportedOperationException.
List<Integer> immutableList = List.of(10, 20, 30, 40);
// To get a mutable ArrayList from List.of()
ArrayList<Integer> mutableFromImmutable = new ArrayList<>(List.of(1, 2, 3));
Initializing with List.of() (Java 9+)
List.of() is optimized for small to medium-sized lists and provides better performance and memory footprint compared to Arrays.asList() for immutable lists.Using Java 8 Streams (Flexible and Powerful)
For more complex initialization scenarios, especially when elements need to be generated or transformed, Java 8 Streams provide a powerful and flexible approach. You can create a stream from various sources and then collect the elements into an ArrayList using Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new).
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
// From a stream of elements
ArrayList<String> streamList = Stream.of("One", "Two", "Three")
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
// Generating a list of numbers
ArrayList<Integer> generatedList = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 5)
.boxed()
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
Initializing with Java 8 Streams
flowchart TD
A[Start]
B["Source (e.g., `Stream.of()`, `Arrays.asList()`, `IntStream`)"]
C["Intermediate Operations (e.g., `map()`, `filter()`)"]
D["Terminal Operation: `collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new))`"]
E[Result: Initialized ArrayList]
A --> B
B --> C
C --> D
D --> EStream-based ArrayList Initialization Flow
Choosing the Right Method
The best method depends on your specific needs regarding mutability, Java version, and the complexity of element generation. The following table summarizes the key characteristics:
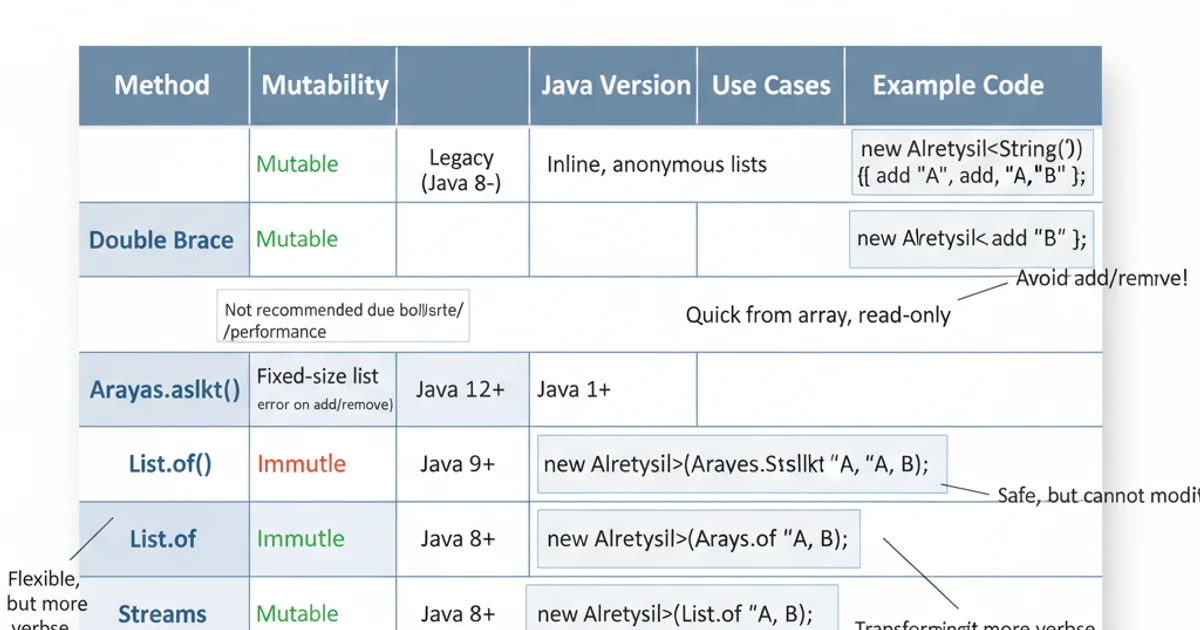
Comparison of ArrayList Initialization Methods
For most modern Java applications, new ArrayList<>(List.of(...)) or new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(...)) are the preferred concise ways to initialize a mutable ArrayList. If you need an immutable list, List.of() is the clear winner. Avoid double brace initialization due to its hidden costs.