What is the difference between Socket and ServerSocket?
Categories:
Socket vs. ServerSocket: Understanding Network Communication in Java
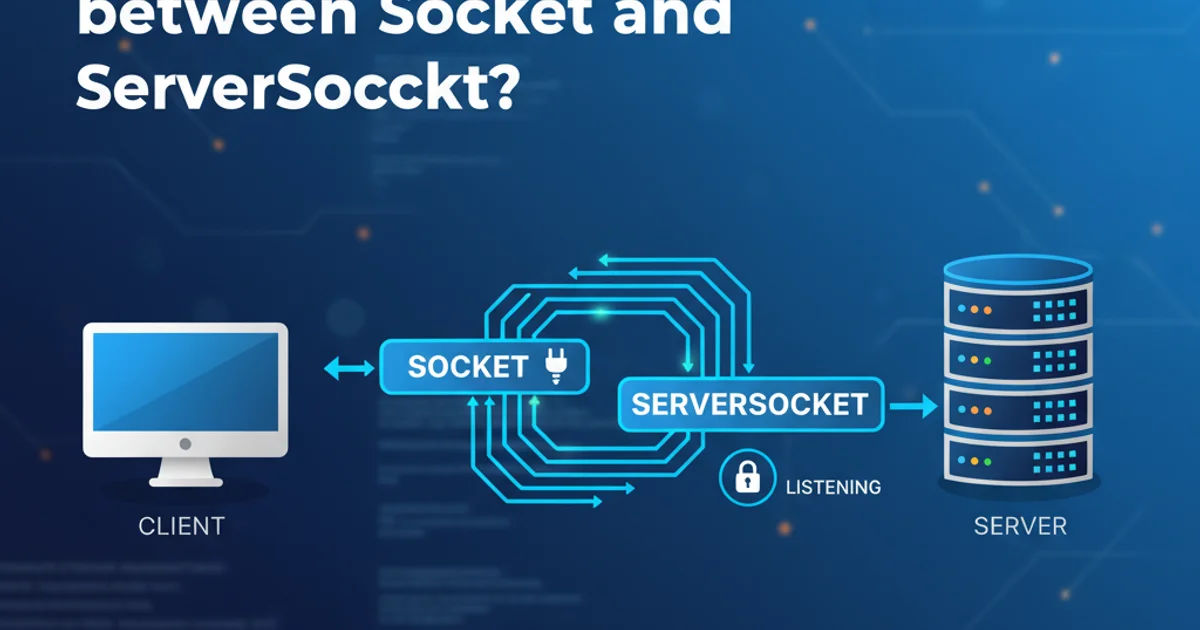
Explore the fundamental differences between Java's Socket and ServerSocket classes, and learn how they facilitate client-server network communication.
In Java, network programming relies heavily on two core classes: Socket and ServerSocket. While both are essential for establishing communication channels over a network, they serve distinct roles in the client-server architecture. Understanding their individual responsibilities and how they interact is crucial for building robust networked applications.
The ServerSocket: The Listener
The ServerSocket class is used by the server application to listen for incoming client connection requests. It acts as a welcoming gatekeeper, waiting for clients to initiate contact. When a client attempts to connect, the ServerSocket accepts the connection and then creates a new Socket object to handle the communication with that specific client. This allows the ServerSocket to continue listening for other clients while the newly created Socket manages the ongoing conversation.
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SimpleServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 12345;
try (ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port)) {
System.out.println("Server listening on port " + port);
while (true) {
Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept(); // Blocks until a client connects
System.out.println("Client connected from: " + clientSocket.getInetAddress());
// Handle client communication in a new thread or method
// For simplicity, we just close it here
clientSocket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Server exception: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Basic Java ServerSocket example demonstrating how to listen for client connections.
ServerSocket and Socket objects in a try-with-resources statement to ensure they are properly closed, preventing resource leaks.The Socket: The Communicator
The Socket class represents an endpoint for communication between two machines. On the client side, a Socket is used to initiate a connection to a ServerSocket on a specific host and port. On the server side, a Socket is created by the ServerSocket.accept() method to handle the established connection with a client. Once a connection is established, both the client and server use their respective Socket objects to send and receive data streams.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SimpleClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String hostname = "localhost";
int port = 12345;
try (Socket socket = new Socket(hostname, port)) {
System.out.println("Connected to server: " + hostname + ":" + port);
// For sending data to the server
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true);
out.println("Hello from client!");
// For receiving data from the server
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String response = in.readLine();
System.out.println("Server response: " + response);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Client exception: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Basic Java Socket example demonstrating how a client connects and sends/receives data.
Key Differences and Interaction
The fundamental difference lies in their roles: ServerSocket is for listening and accepting connections, while Socket is for establishing and maintaining a connection. Think of ServerSocket as a telephone operator waiting for calls, and Socket as the actual telephone line used for a conversation once a call is connected. A single ServerSocket can manage multiple client Socket connections, typically by handing off each new connection to a separate thread for processing.
sequenceDiagram
participant Client
participant ServerSocket
participant ServerSocket_Instance
participant Client_Socket
participant Server_Socket
Client->>ServerSocket: Connection Request (host:port)
ServerSocket->>ServerSocket_Instance: Listens for connections
ServerSocket_Instance->>ServerSocket: Accepts connection
ServerSocket->>Server_Socket: Creates new Socket for client
activate Server_Socket
ServerSocket->>ServerSocket_Instance: Continues listening
Client->>Client_Socket: Establishes connection
activate Client_Socket
Client_Socket-->>Server_Socket: Data Exchange
Server_Socket-->>Client_Socket: Data Exchange
deactivate Client_Socket
deactivate Server_SocketSequence diagram illustrating the interaction between Client, ServerSocket, and Socket objects during connection establishment and data exchange.
Socket returned by ServerSocket.accept() to handle client communication independently.