Run a Command Prompt command from Desktop Shortcut
Categories:
Run a Command Prompt Command from a Desktop Shortcut
Learn how to create a desktop shortcut that executes a specific Command Prompt (CMD) command or script, streamlining your workflow and automating repetitive tasks in Windows.
Creating a desktop shortcut to run a Command Prompt command can significantly boost your productivity. Instead of opening CMD, typing out a command, and pressing Enter, you can simply double-click an icon. This article will guide you through the process of setting up such shortcuts for various use cases, from simple commands to executing batch files.
Understanding the 'target' Field
The core of creating a command-line shortcut lies in configuring the 'Target' field of the shortcut's properties. This field specifies what program to run and with what arguments. For Command Prompt commands, you'll typically invoke cmd.exe and pass your desired command using the /C or /K switch.
cmd.exe /C "your_command_here"
cmd.exe /K "your_command_here"
Basic structure for running commands via cmd.exe
/C switch executes the command and then terminates the Command Prompt window. The /K switch executes the command and keeps the Command Prompt window open, which is useful for observing output or running subsequent commands.Creating a Basic Command Shortcut
Let's start with a simple example: creating a shortcut to ping Google's DNS server. This demonstrates the fundamental steps involved in setting up any command-line shortcut.
1. Right-click on your Desktop
Select 'New' > 'Shortcut' from the context menu.
2. Enter the command in the 'Type the location of the item' field
For our ping example, you would type: cmd.exe /K ping 8.8.8.8. Remember to use /K if you want the window to stay open to see the ping results.
3. Click 'Next'
Provide a meaningful name for your shortcut, such as 'Ping Google DNS'.
4. Click 'Finish'
Your new shortcut will appear on the desktop. Double-click it to execute the command.
flowchart TD
A[Right-click Desktop] --> B{New > Shortcut}
B --> C["Enter Target: cmd.exe /K ping 8.8.8.8"]
C --> D[Click Next]
D --> E[Name Shortcut]
E --> F[Click Finish]
F --> G[Double-click Shortcut]Workflow for creating a basic command prompt shortcut
Executing More Complex Commands and Batch Files
For commands with spaces, special characters, or multiple commands, proper quoting is essential. You can also use shortcuts to execute batch files (.bat or .cmd) which encapsulate a series of commands.
cmd.exe /C "echo Hello World & pause"
cmd.exe /C ""C:\Program Files\My App\app.exe" --arg1 value"
Examples of commands requiring careful quoting
.bat file, or use cmd.exe /C "path\to\your\script.bat" for more control over the CMD window behavior.Advanced Shortcut Properties
Beyond the 'Target' field, shortcut properties offer additional customization options. You can change the icon, set a 'Start in' directory, or even run the command as an administrator.
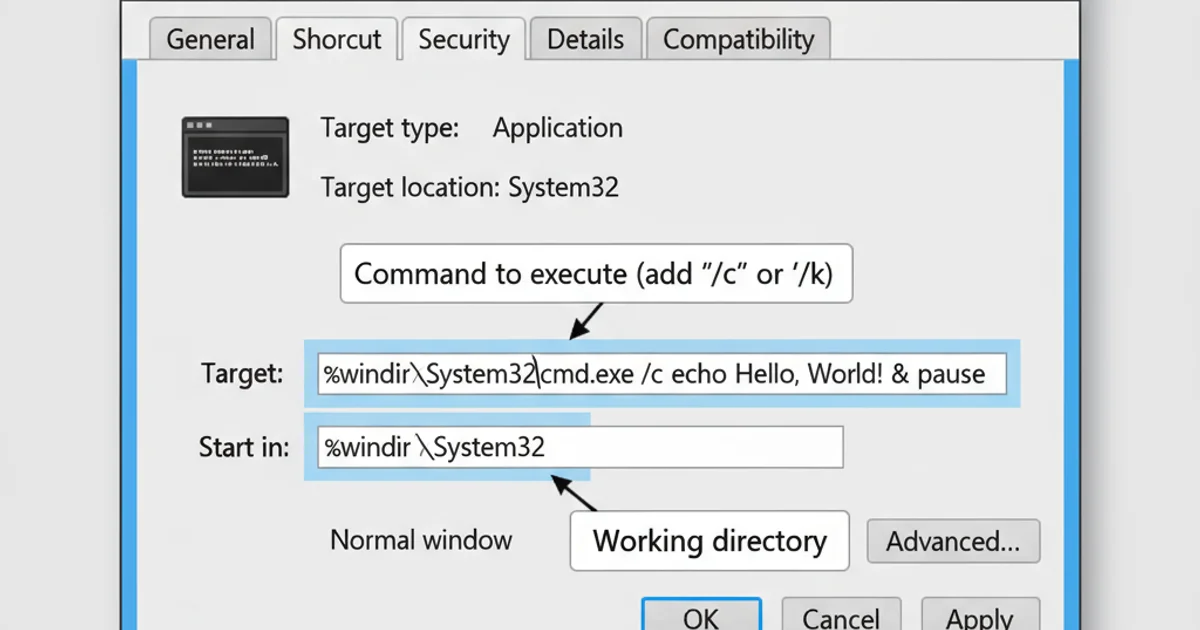
Shortcut Properties window in Windows
1. Right-click the created shortcut
Select 'Properties' from the context menu.
2. Configure 'Start in'
In the 'Shortcut' tab, the 'Start in' field specifies the working directory for the command. This is crucial if your command or script relies on relative paths.
3. Change Icon (Optional)
Click 'Change Icon...' to select a different visual representation for your shortcut.
4. Run as Administrator (Optional)
Click the 'Advanced...' button and check 'Run as administrator' if the command requires elevated privileges. You will be prompted by User Account Control (UAC) when running the shortcut.