XPath:: Get following Sibling
Categories:
Mastering XPath: Selecting Following Sibling Elements
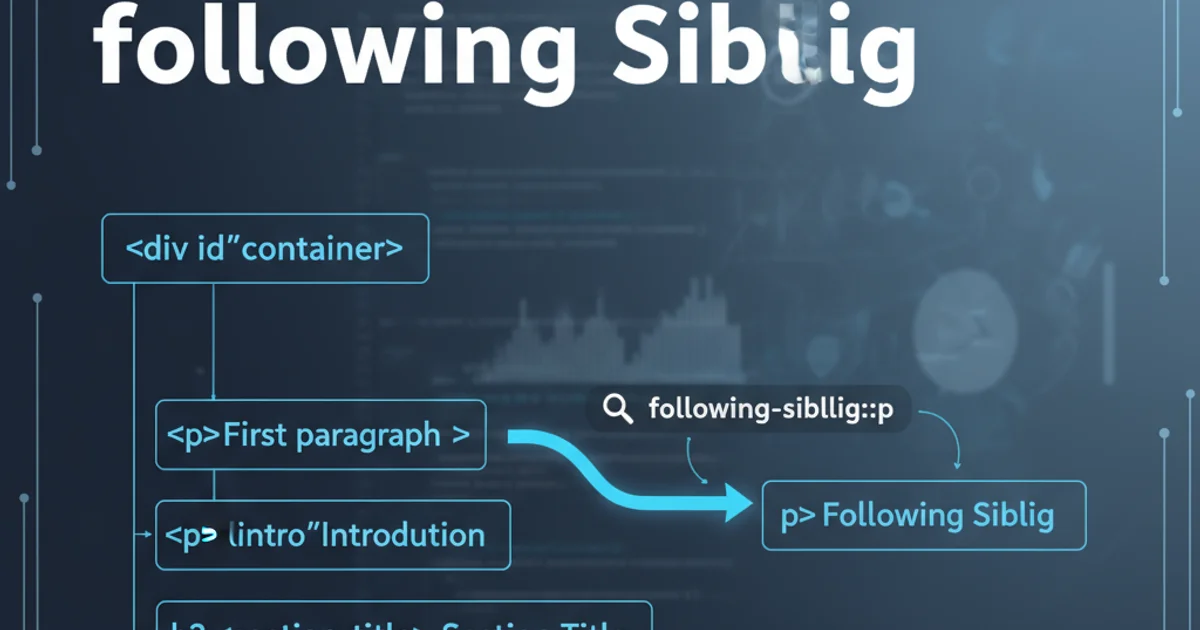
Learn how to effectively use XPath to navigate and select elements that are direct siblings following a specific node in an HTML or XML document. This guide covers various scenarios and provides practical examples.
XPath is a powerful language for navigating XML and HTML documents. One common task is to select elements that appear immediately after a given element, known as 'following siblings'. This article will delve into the following-sibling:: axis, explaining its usage, common pitfalls, and how to apply it effectively in your web scraping or document processing tasks.
Understanding the following-sibling:: Axis
The following-sibling:: axis selects all siblings that come after the context node, sharing the same parent. It's crucial to understand that 'sibling' implies they are at the same level in the document tree and have the same direct parent. This differs from following::, which selects all nodes that appear after the context node in document order, regardless of parentage.
flowchart TD
A[HTML Document] --> B(Body)
B --> C(Div 1)
B --> D(Div 2)
B --> E(Div 3)
C -- "following-sibling::*" --> D
C -- "following-sibling::*" --> E
D -- "following-sibling::*" --> E
style C fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style D fill:#ccf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style E fill:#ccf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2pxVisualizing the following-sibling:: axis in an HTML structure. If 'Div 1' is the context node, 'Div 2' and 'Div 3' are its following siblings.
Basic Usage and Syntax
The basic syntax for selecting following siblings involves specifying the context node, followed by following-sibling:: and then the node test (e.g., * for any element, or a specific tag name like div).
// Select all following sibling elements of the current node
./following-sibling::*
// Select all following sibling 'div' elements of the current node
./following-sibling::div
// Select the first following sibling 'p' element of a 'h2' with specific text
//h2[contains(text(), 'Introduction')]/following-sibling::p[1]
Basic XPath expressions for selecting following siblings.
following-sibling:: only considers elements that are after the context node in the document order. It does not look backwards or at descendants.Advanced Scenarios and Filtering
You can combine following-sibling:: with predicates to filter the selected siblings based on their attributes, text content, or position. This allows for highly specific selections, which is often necessary in complex HTML structures.
// Select all following sibling 'li' elements that have a 'class' attribute of 'active'
./following-sibling::li[@class='active']
// Select the following sibling 'div' that contains a 'span' with specific text
./following-sibling::div[./span[text()='Important Info']]
// Select the second following sibling 'p' element
./following-sibling::p[2]
Advanced XPath examples using predicates to filter following siblings.
[1] or [2] with following-sibling::. The position is relative to the set of all following siblings, not just those matching a specific tag name unless the tag name is part of the axis step itself (e.g., following-sibling::p[1] selects the first p among following siblings, while following-sibling::*[1] selects the very first element of any type among following siblings).