Suggestions for a Web application for a group project
Categories:
Choosing the Right Web Application for Your Group Project
Explore practical web application ideas for group projects, focusing on PHP, database integration, and essential features for collaborative development.
Group projects are an excellent way to learn and apply web development skills. When choosing a web application idea, it's crucial to select something that is achievable within your timeframe, allows for clear division of labor, and provides opportunities to implement various technologies. This article provides several suggestions, focusing on PHP as the backend language, and outlines key features and architectural considerations.
Project Idea 1: Collaborative Task Management System
A task management system is a classic project that offers a wide range of features to implement. It allows users to create projects, assign tasks, set deadlines, and track progress. This idea is particularly good for group work as different team members can focus on different modules (e.g., user authentication, project management, task assignment, reporting).
flowchart TD
A[User Login/Registration] --> B{Authentication Service}
B --> C[Dashboard]
C --> D[Project Management]
D --> D1[Create/Edit Project]
D --> D2[View Projects]
C --> E[Task Management]
E --> E1[Create/Edit Task]
E --> E2[Assign Task]
E --> E3[Update Task Status]
C --> F[User Profile]
F --> F1[Edit Profile]
F --> F2[View Assigned Tasks]
D1 --> G(Database)
D2 --> G
E1 --> G
E2 --> G
E3 --> G
F1 --> G
F2 --> GFlowchart for a Collaborative Task Management System
Key features for this project would include user authentication (login, registration, password reset), CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations for projects and tasks, user roles (e.g., admin, project manager, team member), and potentially real-time updates using WebSockets if you want to explore more advanced concepts. PHP would handle all server-side logic, interacting with a MySQL or PostgreSQL database.
<?php
// Example: Basic PHP for creating a new task
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] === 'POST') {
$project_id = $_POST['project_id'] ?? null;
$task_name = $_POST['task_name'] ?? null;
$assigned_to = $_POST['assigned_to'] ?? null;
$due_date = $_POST['due_date'] ?? null;
if ($project_id && $task_name && $assigned_to && $due_date) {
// Connect to database (using PDO for example)
$pdo = new PDO('mysql:host=localhost;dbname=task_manager', 'user', 'password');
$stmt = $pdo->prepare("INSERT INTO tasks (project_id, name, assigned_to, due_date, status) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, 'pending')");
$stmt->execute([$project_id, $task_name, $assigned_to, $due_date]);
echo "Task created successfully!";
} else {
echo "Error: All fields are required.";
}
}
?>
Project Idea 2: Simple E-commerce Platform for Digital Goods
An e-commerce platform, even a simplified one, provides a robust learning experience. Focusing on digital goods (e.g., e-books, software licenses, music) simplifies the logistics by removing physical shipping, allowing you to concentrate on core e-commerce functionalities like product listings, shopping cart, checkout process, and order management. This project can be divided into frontend development (product display, cart UI) and backend development (product management, order processing, user accounts).
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant Browser
participant PHP_Backend
participant Database
User->>Browser: View Products
Browser->>PHP_Backend: Request /products
PHP_Backend->>Database: SELECT * FROM products
Database-->>PHP_Backend: Product Data
PHP_Backend-->>Browser: Render Product List
User->>Browser: Add to Cart
Browser->>PHP_Backend: POST /cart/add {product_id, quantity}
PHP_Backend->>Database: INSERT/UPDATE cart_items
Database-->>PHP_Backend: Success
PHP_Backend-->>Browser: Cart Updated Confirmation
User->>Browser: Checkout
Browser->>PHP_Backend: POST /checkout {cart_data, payment_info}
PHP_Backend->>PHP_Backend: Validate Payment
PHP_Backend->>Database: Create Order, Clear Cart
Database-->>PHP_Backend: Order ID
PHP_Backend-->>Browser: Order ConfirmationSequence Diagram for E-commerce Checkout Process
Essential features include user registration/login, product catalog display, shopping cart functionality, a simplified checkout process (perhaps simulating payment without actual integration), and an order history for users. On the administrative side, you'd need features to add/edit/delete products and view orders. PHP would manage product data, user sessions, and order processing, with a database storing all relevant information.
Project Idea 3: Online Recipe Sharing Platform
A recipe sharing platform allows users to create, share, and discover recipes. This project is engaging and offers opportunities for implementing search, filtering, user profiles, and social features like comments and ratings. It's also visually appealing, allowing for creative frontend design. The backend would primarily manage user data, recipe data, and interactions.
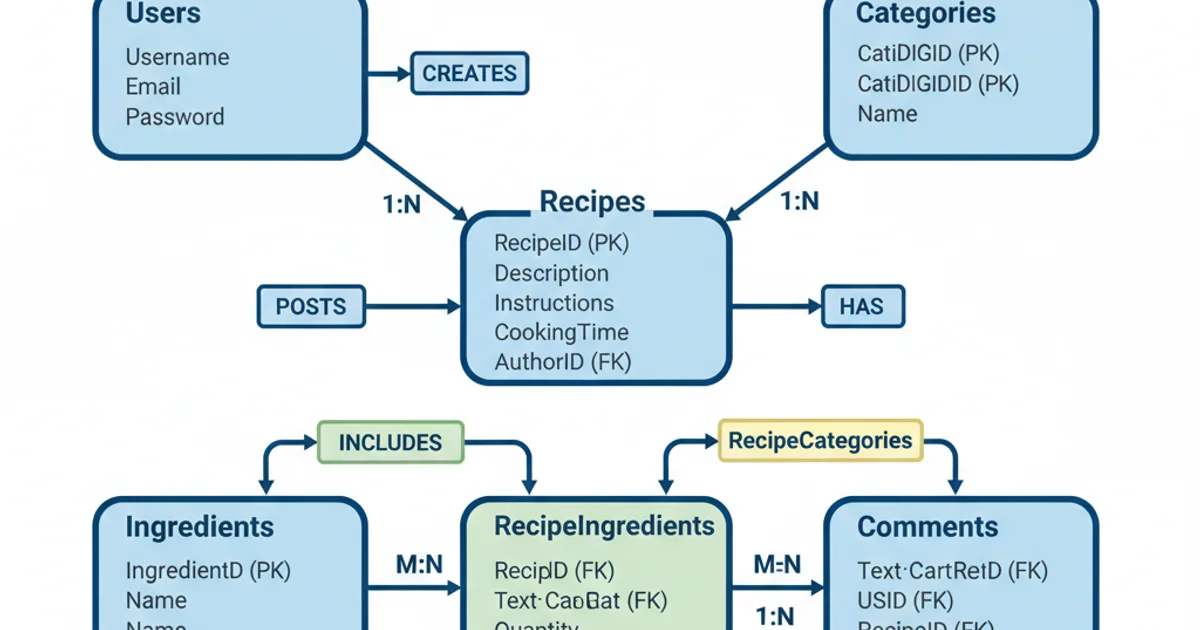
Conceptual Data Model for a Recipe Sharing Platform
Core functionalities would involve user authentication, recipe CRUD operations (including ingredients and instructions), categorization of recipes, a search function with filters (e.g., by cuisine, ingredient, difficulty), and user comments/ratings. You could also add features like 'favorite recipes' or 'meal planner'. PHP would handle all server-side logic, interacting with a database to store recipes, users, and their relationships.
1. Define Scope and Features
Clearly outline the minimum viable product (MVP) features and potential stretch goals. This helps manage expectations and keeps the project focused.
2. Design Database Schema
Create an Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) to map out your database tables and their relationships. This is crucial for a well-structured application.
3. Set Up Development Environment
Ensure all team members have a consistent development environment (e.g., XAMPP, Docker, or a shared cloud environment) with PHP and a database.
4. Divide Tasks and Responsibilities
Break down the project into smaller, manageable tasks and assign them to team members based on their strengths and learning goals. Use version control (Git) religiously.
5. Implement Core Functionality
Start with user authentication and the primary CRUD operations for your main entities. Build incrementally and test frequently.
6. Integrate Frontend and Backend
Connect your HTML/CSS/JavaScript frontend with your PHP backend, ensuring data flows correctly and user interfaces are responsive.
7. Test and Refine
Thoroughly test all features, fix bugs, and gather feedback. Refine the UI/UX and optimize performance where necessary.