Difference Between If and Else If?
Categories:
Understanding 'if' vs. 'else if' in Java
Explore the fundamental differences between 'if' and 'else if' statements in Java, how they control program flow, and best practices for their use.
Conditional statements are the backbone of decision-making in programming. In Java, if and else if are crucial constructs that allow your code to execute different blocks based on whether certain conditions are met. While they both evaluate conditions, their interaction within a sequence significantly impacts program behavior. Understanding this distinction is key to writing efficient and logical code.
The 'if' Statement: Independent Conditions
An if statement evaluates a single condition. If the condition is true, the code block immediately following it is executed. If the condition is false, that block is skipped. When you have multiple if statements in sequence, each one is evaluated independently of the others. This means that if the condition for the first if statement is true, its block executes, and then the program proceeds to evaluate the next if statement, and so on. All if blocks whose conditions are true will execute.
int score = 85;
if (score >= 70) {
System.out.println("Passed the exam.");
}
if (score >= 80) {
System.out.println("Achieved a good score.");
}
if (score >= 90) {
System.out.println("Achieved an excellent score.");
}
Example of independent 'if' statements
In the example above, if score is 85, both "Passed the exam." and "Achieved a good score." will be printed because both if conditions are met independently. The condition score >= 90 is false, so its block is skipped.
The 'else if' Statement: Mutually Exclusive Conditions
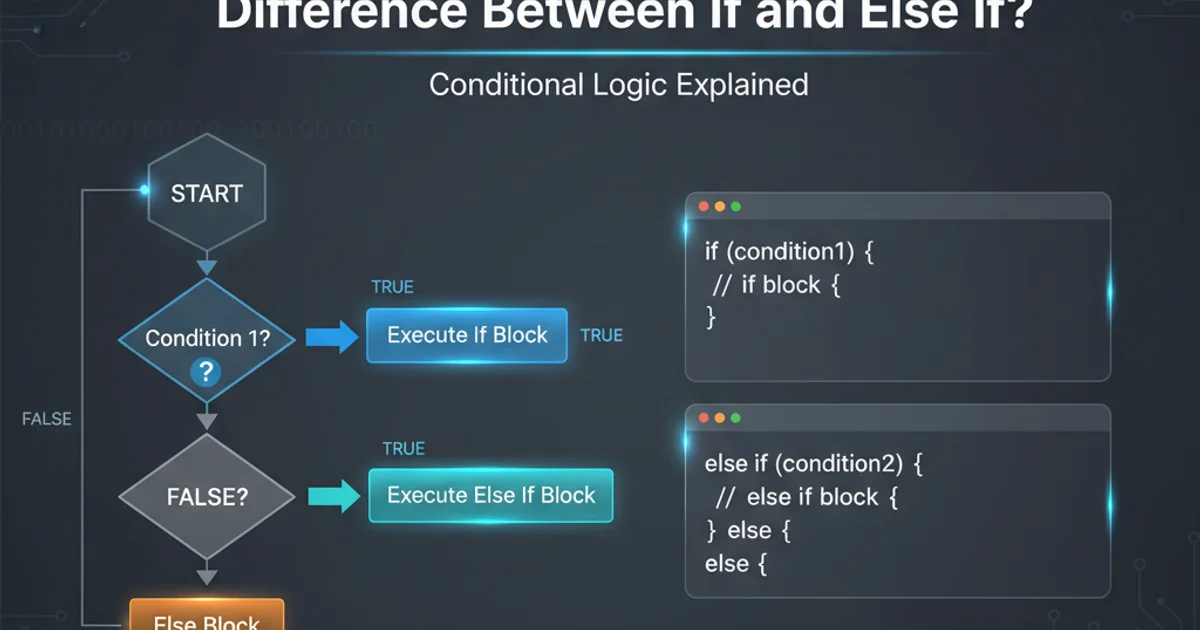
The else if statement is used in conjunction with an initial if statement (and optionally other else if statements) to create a chain of mutually exclusive conditions. Once an if or else if condition in the chain evaluates to true, its corresponding code block is executed, and the entire if-else if-else chain is exited. No further else if or else conditions in that specific chain will be evaluated. This ensures that only one block of code within the chain will ever execute.
int temperature = 25;
if (temperature > 30) {
System.out.println("It's very hot!");
} else if (temperature > 20) {
System.out.println("It's warm.");
} else if (temperature > 10) {
System.out.println("It's mild.");
} else {
System.out.println("It's cold.");
}
Example of an 'if-else if-else' chain
In this if-else if-else chain, if temperature is 25, the first condition (temperature > 30) is false. The program then checks the next condition (temperature > 20), which is true. "It's warm." is printed, and the rest of the else if and else blocks are skipped. Only one message is printed.
flowchart TD
A[Start] --> B{Condition 1?}
B -- Yes --> C[Execute Block 1]
B -- No --> D{Condition 2?}
D -- Yes --> E[Execute Block 2]
D -- No --> F{Condition 3?}
F -- Yes --> G[Execute Block 3]
F -- No --> H[Execute Else Block]
C --> I[End]
E --> I
G --> I
H --> IFlowchart illustrating the 'if-else if-else' decision process
if-else if chain. More specific or restrictive conditions should generally come before more general ones to ensure the correct block is executed. For example, checking for score >= 90 before score >= 70.Key Differences Summarized
The core distinction lies in how subsequent conditions are handled. Independent if statements allow multiple blocks to execute if their conditions are met, whereas an if-else if chain guarantees that only one block will execute from the entire sequence.
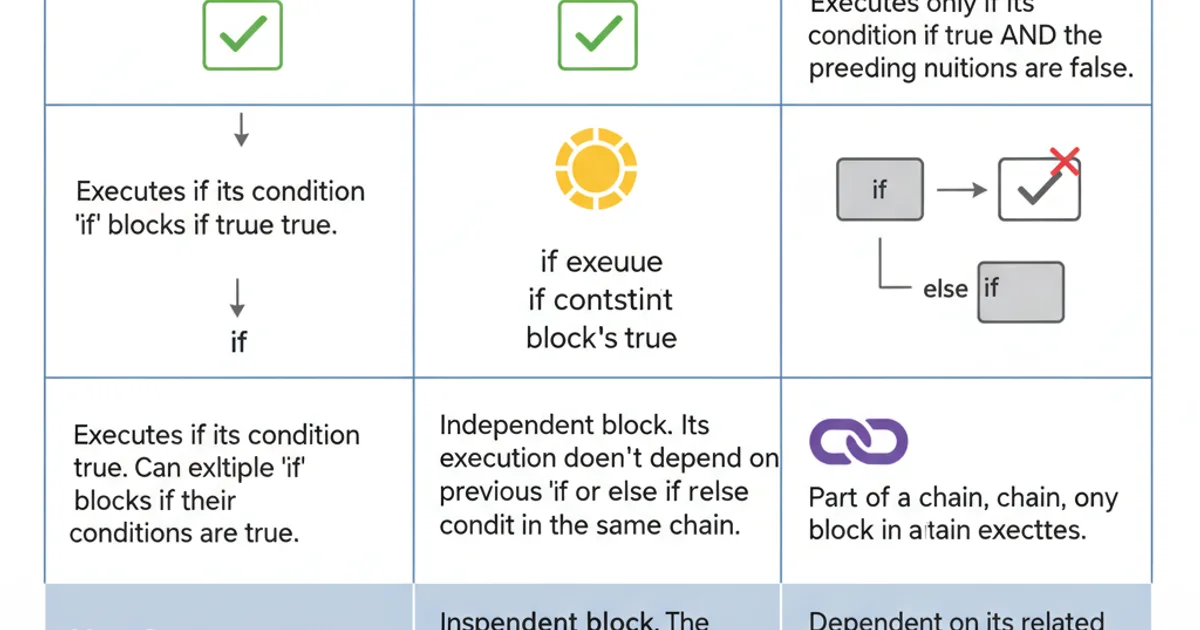
Comparison of 'if' vs. 'else if' statements
Choosing between independent if statements and an if-else if chain depends entirely on your program's logic. If multiple conditions can (and should) be true simultaneously, use separate if statements. If only one condition out of a set can be true, or if you want to stop checking once a condition is met, use an if-else if chain.