ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'sklearn'
Categories:
Resolving 'ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'sklearn'' in Python
This article provides comprehensive solutions for the common 'ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'sklearn'' when working with Python and scikit-learn, covering installation, environment management, and common pitfalls.
The ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'sklearn' is a frequently encountered issue for Python developers, especially those new to machine learning or working with virtual environments. This error indicates that the Python interpreter cannot find the scikit-learn library, which is typically imported as sklearn. This guide will walk you through the common causes and provide step-by-step solutions to get your machine learning projects back on track.
Understanding the Root Cause
Before diving into solutions, it's crucial to understand why this error occurs. Python looks for modules in specific locations defined by its sys.path. If scikit-learn is not installed in an accessible location for your current Python environment, or if you're using the wrong environment, the interpreter won't find it. The most common reasons include:
- Scikit-learn not installed: The package simply hasn't been installed in your Python environment.
- Incorrect environment: You have multiple Python installations or virtual environments, and
scikit-learnis installed in one, but you're running your script from another. - Installation issues: The installation process failed or was incomplete.
- IDE/Editor misconfiguration: Your IDE (e.g., VS Code, PyCharm) might be configured to use a different Python interpreter than the one where
scikit-learnis installed.
flowchart TD
A[Start Python Script] --> B{Is 'sklearn' in sys.path?}
B -- No --> C[ModuleNotFoundError]
B -- Yes --> D[Import 'sklearn' Successfully]
C --> E{Check Installation}
C --> F{Check Active Environment}
E --> G[Install 'scikit-learn']
F --> H[Activate Correct Environment]
G --> D
H --> DFlowchart illustrating the cause and resolution path for ModuleNotFoundError.
Solution 1: Installing Scikit-learn
The most straightforward solution is to ensure scikit-learn is properly installed in your active Python environment. We'll cover both pip and conda installation methods.
pip install scikit-learn
Installing scikit-learn using pip.
conda install scikit-learn
Installing scikit-learn using conda (for Anaconda/Miniconda users).
pip install scikit-learn (not pip install sklearn) as the package name for installation is scikit-learn, while the import name is sklearn.Solution 2: Verifying Your Python Environment
Often, the module is installed, but you're running your script with a different Python interpreter. This is especially common when using virtual environments (like venv or conda environments) or if you have multiple Python versions installed on your system.
1. Check Active Python Interpreter
Open your terminal or command prompt and run which python (Linux/macOS) or where python (Windows) to see which Python executable is currently active. Then, run python -c "import sys; print(sys.path)" to see where Python is looking for modules.
2. Verify Scikit-learn Installation
From the same terminal, run pip show scikit-learn (or conda list scikit-learn). If it's installed, this command will show details like its version and location. If it's not found, it confirms the package isn't in the active environment.
3. Activate the Correct Environment (if applicable)
If you're using a virtual environment (e.g., venv or conda), ensure it's activated before running your script. For venv, navigate to your project directory and run source venv/bin/activate (Linux/macOS) or .\venv\Scripts\activate (Windows PowerShell). For conda, use conda activate your_env_name.
4. Run Your Script
After activating the correct environment and confirming scikit-learn is installed, try running your Python script again.
Solution 3: IDE Configuration
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) like VS Code or PyCharm manage their own Python interpreters. If your IDE is not configured to use the same interpreter where scikit-learn is installed, you'll encounter the ModuleNotFoundError.
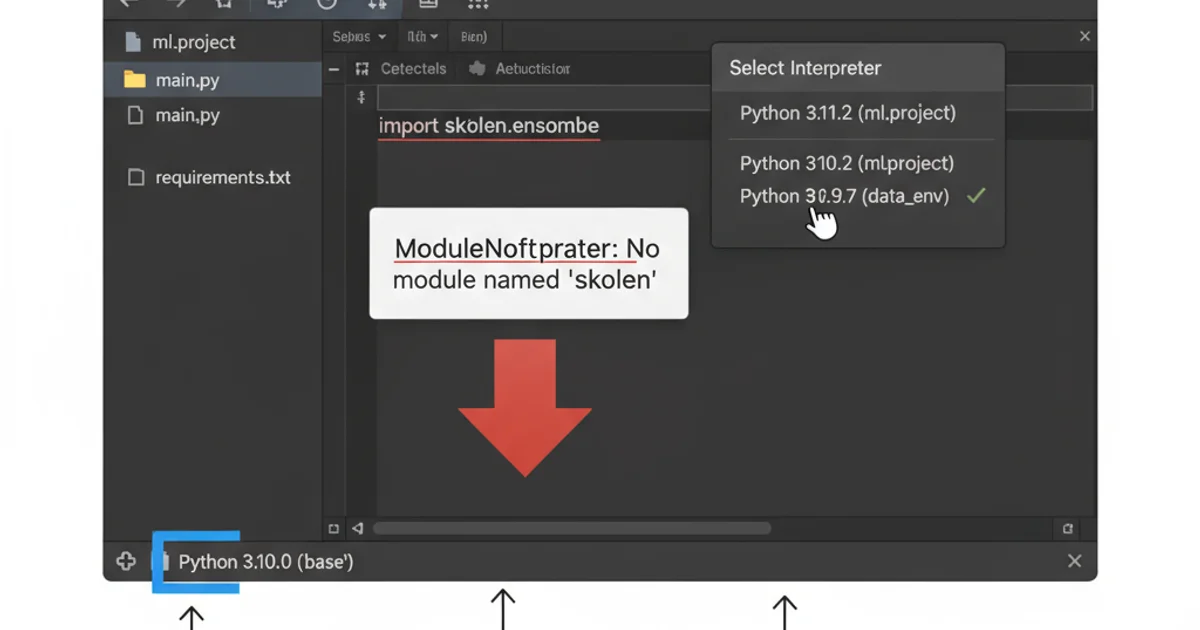
Selecting the correct Python interpreter in VS Code.
File > Settings > Project: [Your Project Name] > Python Interpreter and select or add the correct interpreter. Ensure the chosen interpreter lists scikit-learn among its installed packages.Troubleshooting Common Scenarios
Here are some additional tips for specific situations:
sudo pip install unless absolutely necessary, as this can lead to permission issues and conflicts with system-wide Python installations. Always prefer virtual environments.If you're using Jupyter Notebooks or JupyterLab, ensure that the kernel you're running your notebook with corresponds to the Python environment where scikit-learn is installed. You can often change the kernel from the notebook interface (e.g., Kernel > Change Kernel). If scikit-learn is installed in a conda environment, you might need to install ipykernel in that environment and register it with Jupyter:
conda install ipykernel
python -m ipykernel install --user --name=my_env_name --display-name "Python (my_env_name)"
Replace my_env_name with the actual name of your conda environment.
By systematically checking your installation, active environment, and IDE configuration, you should be able to resolve the ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'sklearn' and successfully import scikit-learn into your Python projects.