OpenCV function list
Categories:
Mastering OpenCV: A Comprehensive Guide to Essential Functions

Explore the core functionalities of OpenCV, the leading open-source computer vision library. This article provides an overview of key functions for image processing, object detection, and more, empowering you to build robust vision applications.
OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision Library) is an indispensable tool for anyone working with image and video data. From basic image manipulation to advanced machine learning algorithms, OpenCV offers a vast array of functions that simplify complex tasks. Understanding its core components is crucial for developing efficient and powerful computer vision applications. This guide will walk you through some of the most frequently used and fundamental functions, categorized by their primary use cases.
Core Image Operations: Loading, Displaying, and Saving
The foundation of any computer vision project involves handling images. OpenCV provides straightforward functions to read images from various formats, display them in a window, and save processed images back to disk. These operations are often the first steps in any image processing pipeline.
flowchart TD
A[Start Application] --> B["cv2.imread(filepath)"]
B --> C{Image Loaded?}
C -- Yes --> D["cv2.imshow(window_name, image)"]
D --> E["cv2.waitKey(delay)"]
E --> F{Key Pressed or Delay Expired?}
F -- Yes --> G["cv2.imwrite(filepath, image)"]
G --> H["cv2.destroyAllWindows()"]
H --> I[End Application]
C -- No --> J[Error: Image not found/loaded]
J --> IBasic OpenCV Image Workflow: Load, Display, and Save
import cv2
# Load an image
image_path = 'example.jpg'
img = cv2.imread(image_path)
# Check if image was loaded successfully
if img is None:
print(f"Error: Could not load image from {image_path}")
else:
# Display the image
cv2.imshow('Original Image', img)
# Wait for a key press (0 means wait indefinitely)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# Save the image (e.g., as a grayscale version)
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imwrite('grayscale_example.jpg', gray_img)
# Destroy all OpenCV windows
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Python example for loading, displaying, and saving an image using OpenCV.
cv2.imread() reads images in BGR (Blue, Green, Red) format by default, not RGB. This is a common point of confusion for beginners.Image Processing Fundamentals: Manipulation and Enhancement
OpenCV provides a rich set of functions for manipulating and enhancing images. These include operations like resizing, cropping, color space conversions, and applying various filters to reduce noise or detect edges. Mastering these functions is key to preparing images for further analysis or improving their visual quality.
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('example.jpg')
if img is not None:
# Resize image to half its original size
resized_img = cv2.resize(img, (0,0), fx=0.5, fy=0.5)
# Convert to grayscale
gray_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Apply Gaussian blur to reduce noise
blurred_img = cv2.GaussianBlur(img, (5, 5), 0)
# Apply Canny edge detection
edges = cv2.Canny(gray_img, 100, 200)
# Display results
cv2.imshow('Resized Image', resized_img)
cv2.imshow('Grayscale Image', gray_img)
cv2.imshow('Blurred Image', blurred_img)
cv2.imshow('Canny Edges', edges)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
else:
print("Error: Image not loaded.")
Demonstration of common image processing functions: resize, grayscale, blur, and edge detection.
Feature Detection and Object Recognition
Beyond basic processing, OpenCV excels in identifying features within images and recognizing objects. Functions like cv2.findContours(), cv2.HoughLines(), and algorithms for feature descriptors (e.g., SIFT, SURF, ORB) enable sophisticated analysis. While some advanced feature detectors might require extra modules or older versions of OpenCV due to patent restrictions, the library still offers powerful tools for these tasks.
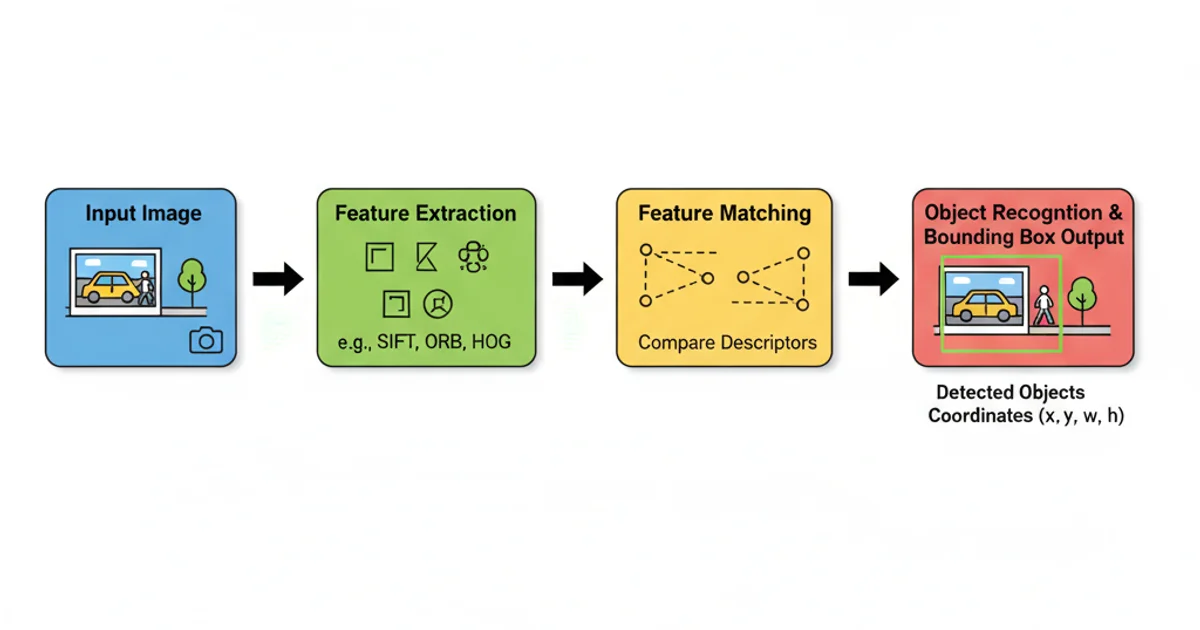
Conceptual flow of feature detection leading to object recognition.
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('shapes.png')
if img is not None:
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
edged = cv2.Canny(blurred, 50, 150)
# Find contours
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# Draw contours on the original image
cv2.drawContours(img, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# Display the result
cv2.imshow('Detected Contours', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
else:
print("Error: Image not loaded.")
Example of using cv2.findContours() to detect and draw shapes in an image.