Safari cannot connect to local URL: http://127.0.0.1:5000
Categories:
Safari Cannot Connect to Localhost: Troubleshooting 127.0.0.1:5000 on macOS
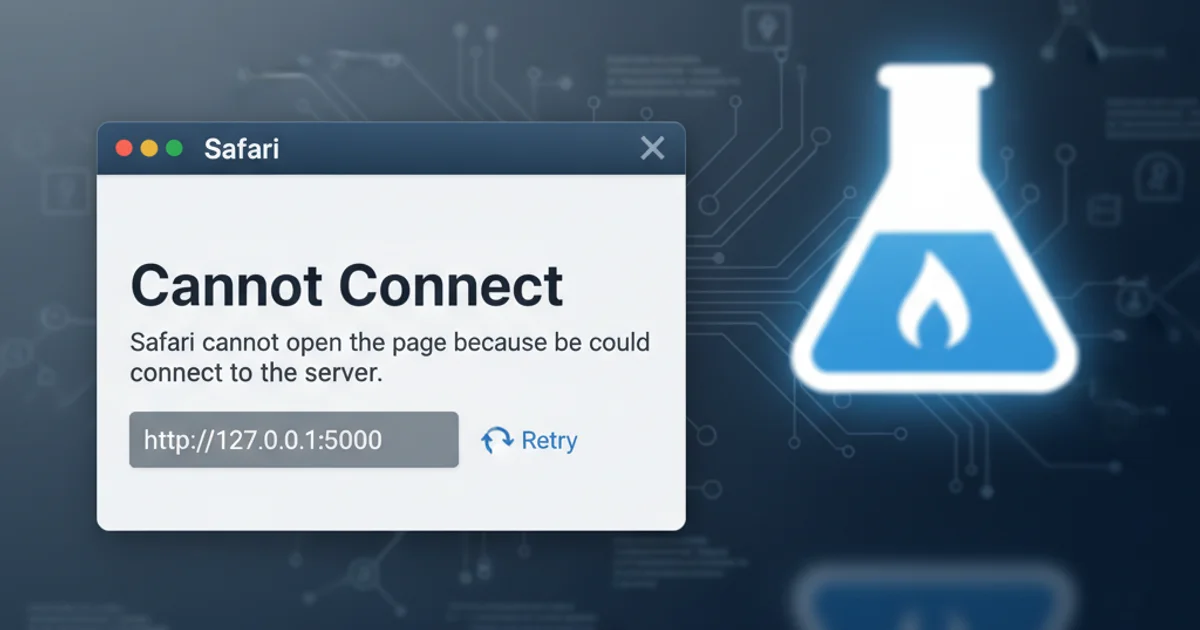
Encountering 'Safari cannot connect to the server' when accessing local Flask applications? This guide helps diagnose and resolve common issues preventing Safari from reaching 127.0.0.1:5000 on macOS.
Developing web applications often involves running a local server, typically on localhost or 127.0.0.1 at a specific port, like 5000 for Flask. While other browsers might connect without issue, Safari on macOS can sometimes present a 'Safari cannot connect to the server' error. This article will walk you through the common causes and solutions for this frustrating problem, focusing on Python Flask applications but applicable to other local server setups.
Understanding the Problem: Why Safari?
Safari's security and networking stack can sometimes behave differently than Chrome or Firefox, especially concerning local network access and DNS resolution. The error 'Safari cannot connect to the server' usually indicates that Safari failed to establish a connection to the specified IP address and port. This could be due to the server not running, firewall restrictions, incorrect network configuration, or even specific browser settings.
flowchart TD
A[Start Flask App] --> B{Is Server Running?}
B -- No --> C[Start Server Correctly]
B -- Yes --> D{Firewall Blocking?}
D -- Yes --> E[Adjust Firewall Rules]
D -- No --> F{Incorrect Host/Port?}
F -- Yes --> G[Verify Flask Host/Port]
F -- No --> H{Browser Cache/Extensions?}
H -- Yes --> I[Clear Cache/Disable Extensions]
H -- No --> J[Network Configuration Issues]
J --> K[Check /etc/hosts, DNS]
K --> L[Safari Connects Successfully]Troubleshooting flow for Safari connection issues to localhost.
Common Causes and Solutions
Let's break down the most frequent reasons why Safari might struggle to connect to your local Flask server and how to fix them.
1. Flask Server Not Binding to Correct Interface
By default, Flask's app.run() might bind to 127.0.0.1 (localhost). While this is usually fine, sometimes explicitly telling Flask to bind to 0.0.0.0 (all available interfaces) can resolve connectivity issues, especially in virtualized or containerized environments, or if there are subtle network configuration differences. Even for a simple local setup, this can sometimes help Safari.
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_world():
return 'Hello, Safari!'
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Explicitly bind to 0.0.0.0 to make it accessible from other IPs
# and sometimes resolves localhost issues with specific browsers.
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000, debug=True)
Running a Flask app with host explicitly set to '0.0.0.0'.
2. macOS Firewall or Security Software
Your macOS firewall or any third-party security software could be blocking incoming connections to port 5000. While less common for 127.0.0.1 (which is internal to your machine), it's worth checking.
1. Check macOS Firewall
Go to System Settings > Network > Firewall. Ensure the firewall is either off (for testing) or configured to allow incoming connections for your Python application.
2. Temporarily Disable Firewall
For testing purposes, you can temporarily disable the firewall. If Safari connects after disabling it, you'll know the firewall is the culprit and can then add an exception for your Flask app.
3. Check Third-Party Security Software
If you have any antivirus or network monitoring tools, check their settings for any rules that might be blocking local network traffic on port 5000.
3. Browser Cache, Extensions, or DNS Issues
Safari's cache or installed extensions can sometimes interfere with local connections. Additionally, issues with DNS resolution (even for localhost) can occur.
1. Clear Safari Cache
Go to Safari > Settings > Privacy > Manage Website Data... and remove data for localhost or 127.0.0.1. You can also go to Develop > Empty Caches (if the Develop menu is enabled via Settings > Advanced).
2. Disable Safari Extensions
Go to Safari > Settings > Extensions and temporarily disable all extensions. Test if the connection works. If it does, re-enable them one by one to find the culprit.
3. Verify /etc/hosts File
Ensure your /etc/hosts file correctly maps localhost to 127.0.0.1. Open Terminal and type cat /etc/hosts. You should see lines like 127.0.0.1 localhost and ::1 localhost.
4. Incorrect Port or IP Address
It might seem obvious, but double-check that you are indeed trying to access http://127.0.0.1:5000 and that your Flask application is configured to run on port 5000. Sometimes, other applications might be using port 5000, causing Flask to start on a different port (e.g., 5001).
lsof -i :5000
Use lsof to check if another process is using port 5000.
If lsof returns a process, that process is using port 5000. You'll need to either stop that process or configure your Flask app to use a different port.
http://127.0.0.1:5001).