Why Use The <html> Tag?
Categories:
The Enduring Importance of the <html> Tag in Web Development

Explore the fundamental role of the <html> tag, its historical significance, and why it remains crucial for modern web standards, accessibility, and browser rendering.
In the vast and ever-evolving landscape of web development, some elements are so foundational that their purpose might seem self-evident, or even redundant. The <html> tag is one such element. Often taken for granted, it serves as the root of every HTML document, encapsulating all other content. But beyond its structural role, why is it truly necessary? This article delves into the core reasons why the <html> tag is not just a convention, but a critical component for proper web page construction, browser interpretation, and adherence to web standards.
The Root Element: Defining the Document
At its most basic, the <html> tag signifies to the browser that the content within it is an HTML document. It acts as the ultimate parent for all other elements, including the <head> and <body>. Without this root, a browser might struggle to correctly parse the document, potentially leading to rendering inconsistencies or unexpected behavior. It establishes the context for the entire page, telling the rendering engine, "Everything inside me is HTML."
flowchart TD
A[Web Server Request] --> B{Browser Receives Data}
B --> C{Is `<!DOCTYPE html>` present?}
C -- Yes --> D{Is `<html>` present?}
C -- No --> E[Quirks Mode Rendering]
D -- Yes --> F[Standard HTML Parsing]
D -- No --> G[Potential Parsing Errors / Inconsistencies]
F --> H[Render Page]
E --> HBrowser's initial parsing flow with <html> and <!DOCTYPE html>
Language Declaration for Accessibility and SEO
One of the most important attributes of the <html> tag is the lang attribute. This attribute specifies the primary language of the document (e.g., lang="en" for English, lang="es" for Spanish). This seemingly small detail has significant implications for accessibility and search engine optimization (SEO).
For accessibility, screen readers and other assistive technologies rely on the lang attribute to correctly pronounce text, apply appropriate linguistic rules, and switch voice profiles. Without it, a screen reader might attempt to read content in the wrong language, making the page unintelligible for users with visual impairments.
From an SEO perspective, search engines use the lang attribute to better understand the content's target audience and serve it to users searching in that specific language. It helps in geo-targeting and ensures your content reaches the right audience globally.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>My Awesome Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome!</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph in English.</p>
</body>
</html>
Example of <html> tag with the lang attribute
lang attribute on your <html> tag. It's a simple yet powerful way to improve accessibility and SEO for your web pages.Browser Compatibility and Standard Mode Rendering
While modern browsers are highly forgiving, omitting the <html> tag (especially in conjunction with the <!DOCTYPE html> declaration) can sometimes trigger 'quirks mode' rendering. Quirks mode is a compatibility mode designed to render old, non-standard web pages. In this mode, browsers might interpret CSS and JavaScript differently, leading to layout issues, inconsistent styling, and unexpected behavior across different browsers.
By explicitly including <html> and the <!DOCTYPE html> declaration, you ensure that the browser renders your page in 'standards mode,' adhering to modern web standards and providing a consistent experience for all users. This is crucial for predictable layouts and robust web applications.
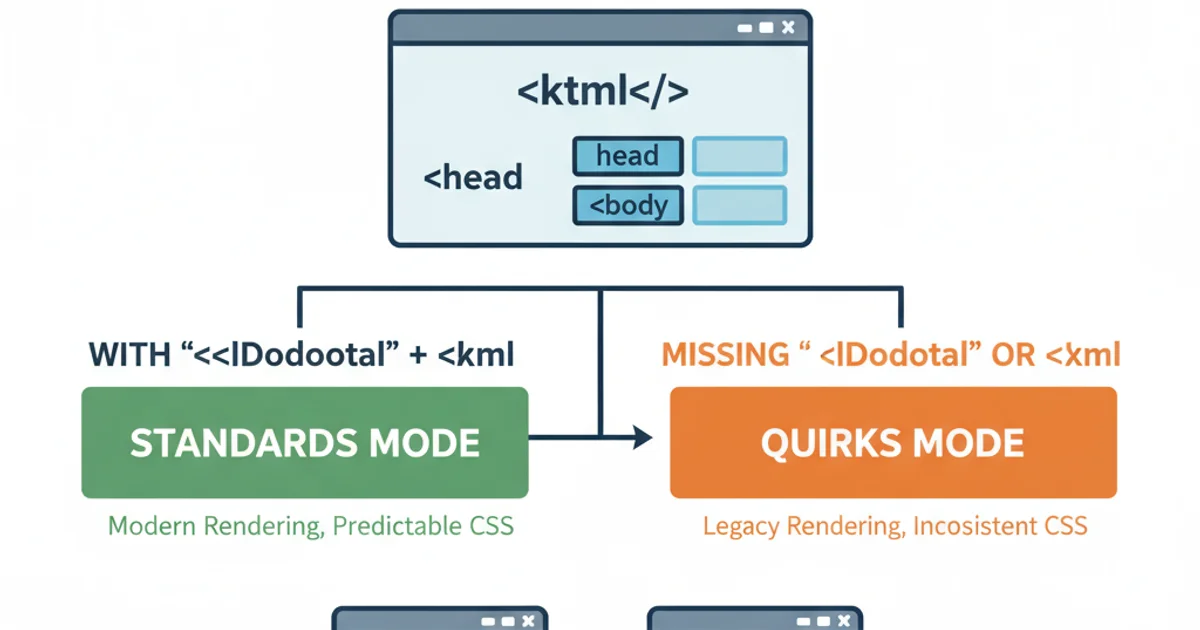
The <html> tag, alongside <!DOCTYPE html>, ensures standards mode rendering.
In conclusion, the <html> tag is far more than just boilerplate. It's the foundational element that defines your document as HTML, enables crucial accessibility features through the lang attribute, and ensures consistent, standards-compliant rendering across browsers. Neglecting it can lead to a cascade of issues, from broken layouts to poor search engine visibility and an inaccessible user experience. Always start your HTML documents with a well-formed <html> tag.