Representational state transfer (REST) and Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP)
Categories:
REST vs. SOAP: Understanding Web Service Communication
Explore the fundamental differences between REST and SOAP, two prominent architectural styles for building web services, and learn when to choose each for your projects.
In the world of distributed systems and web development, communication between different applications is paramount. Representational State Transfer (REST) and Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) are two widely adopted architectural styles and protocols for enabling this communication, often referred to as web services. While both serve the purpose of allowing applications to exchange data, they approach the problem with fundamentally different philosophies, leading to distinct advantages and disadvantages.
What is SOAP?
SOAP is a protocol for exchanging structured information in the implementation of web services. It relies on XML for its message format and typically operates over HTTP, but can also use other protocols like SMTP or TCP. SOAP is highly standardized, offering built-in error handling, security, and reliability features through various extensions (WS-Security, WS-ReliableMessaging, etc.). This makes it a robust choice for enterprise-level applications requiring strict contracts and complex transactions.
sequenceDiagram
participant Client
participant Server
Client->>Server: SOAP Request (XML Envelope)
activate Server
Server-->>Client: SOAP Response (XML Envelope)
deactivate ServerBasic SOAP communication flow
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope
xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding">
<soap:Body xmlns:m="http://www.example.org/stock">
<m:GetStockPrice>
<m:StockName>IBM</m:StockName>
</m:GetStockPrice>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
What is REST?
REST is an architectural style, not a protocol, that defines a set of constraints for how web services should be designed. It emphasizes stateless client-server communication, cacheability, and a uniform interface. RESTful services typically use standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to perform operations on resources, which are identified by URLs. Data formats are flexible, commonly using JSON or XML, with JSON being the most prevalent due to its lightweight nature and ease of parsing in web browsers and mobile applications.
flowchart LR
Client -- GET /users/123 --> Server
Server -- 200 OK (JSON User Data) --> Client
Client -- POST /users (JSON New User) --> Server
Server -- 201 Created --> ClientRESTful API interaction using HTTP methods
{
"id": "123",
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john.doe@example.com"
}
Key Differences and When to Choose Which
The choice between REST and SOAP often comes down to the specific requirements of your project. REST is generally preferred for public APIs, mobile applications, and web applications due to its simplicity, flexibility, and performance. SOAP, with its robust features and strict contracts, is often chosen for enterprise-level applications, legacy systems, and scenarios requiring advanced security and transactional capabilities.
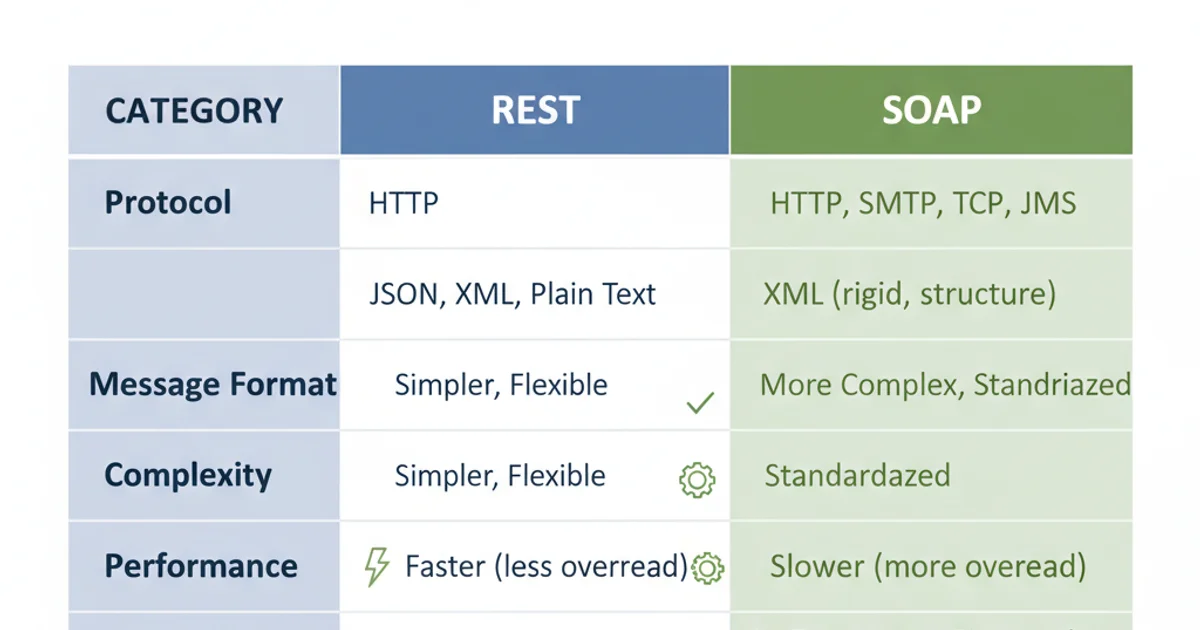
REST vs. SOAP: A comparative overview
Here's a summary of their key differences:
1. Protocol vs. Architectural Style
SOAP is a protocol with strict rules and standards, while REST is an architectural style with a set of guidelines.
2. Message Format
SOAP exclusively uses XML. REST is flexible, commonly using JSON, XML, or plain text.
3. Complexity
SOAP is generally more complex to implement and requires more overhead due to its extensive standards and XML parsing. REST is simpler and lighter.
4. Performance
REST is generally faster and more performant due to smaller message sizes (especially with JSON) and less processing overhead.
5. Security & Reliability
SOAP has built-in security (WS-Security) and reliability (WS-ReliableMessaging) features. REST relies on the underlying transport protocol (HTTPS) for security and implements reliability at the application level.
6. Statefulness
SOAP can be stateful or stateless. REST is inherently stateless, meaning each request is independent.