how to create a square using for loops
Categories:
Drawing Squares with For Loops: A Fundamental Programming Concept
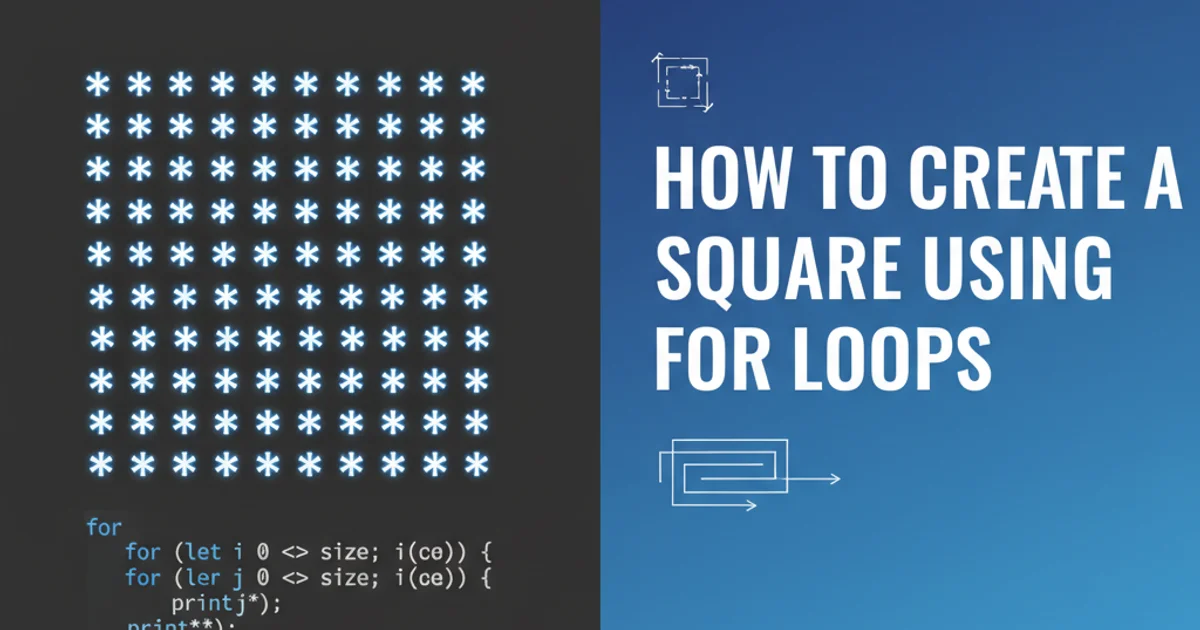
Learn how to construct square patterns using nested for loops in various programming languages, a foundational skill for understanding iterative structures and basic graphics.
Creating geometric shapes using characters in a console is a classic programming exercise that introduces fundamental concepts like iteration, nested loops, and conditional logic. This article will guide you through the process of drawing a perfect square using for loops, primarily focusing on Java, but the principles are transferable to many other languages.
Understanding the Logic: Rows and Columns
To draw a square, we need to think about its dimensions: a certain number of rows and an equal number of columns. Each position within this grid will either be part of the square's outline or its interior. A for loop is ideal for iterating a fixed number of times, making it perfect for handling rows and columns. We'll use two nested for loops: an outer loop to control the rows and an inner loop to control the columns within each row.
flowchart TD
A[Start] --> B{Define Square Size (N)};
B --> C{Outer Loop: Iterate N times for Rows (i)};
C --> D{Inner Loop: Iterate N times for Columns (j)};
D --> E{Print Character (e.g., '*')};
E --> D;
D --> F{Print Newline Character};
F --> C;
C --> G[End];Flowchart illustrating the nested loop logic for drawing a square.
Implementing a Solid Square
A solid square means every position within the N x N grid will be filled with a character, typically an asterisk (*). The outer loop will run N times (for N rows), and for each iteration of the outer loop, the inner loop will also run N times (for N columns). Inside the inner loop, we simply print our chosen character. After the inner loop completes (meaning one row is finished), we print a newline character to move to the next row.
public class SolidSquare {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = 5; // Define the size of the square
// Outer loop for rows
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// Inner loop for columns
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
System.out.print("*"); // Print character for each column
}
System.out.println(); // Move to the next line after each row
}
}
}
Java code to print a solid square of a given size.
Creating a Hollow Square
A hollow square is slightly more complex as it requires a conditional check. We only want to print the character (*) if the current position is on the border of the square. This means if it's the first row (i == 0), the last row (i == size - 1), the first column (j == 0), or the last column (j == size - 1). For all other positions (the interior), we print a space ( ).
public class HollowSquare {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = 5; // Define the size of the square
// Outer loop for rows
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// Inner loop for columns
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
// Check if current position is on the border
if (i == 0 || i == size - 1 || j == 0 || j == size - 1) {
System.out.print("*");
} else {
System.out.print(" "); // Print space for interior
}
}
System.out.println(); // Move to the next line after each row
}
}
}
Java code to print a hollow square of a given size.
Python
def draw_square(size): for i in range(size): for j in range(size): if i == 0 or i == size - 1 or j == 0 or j == size - 1: print("*", end="") else: print(" ", end="") print()
draw_square(5)
C#
using System;
public class HollowSquare { public static void Main(string[] args) { int size = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
if (i == 0 || i == size - 1 || j == 0 || j == size - 1)
{
Console.Write("*");
}
else
{
Console.Write(" ");
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}