Creating new file through Windows Powershell
Categories:
Creating New Files with PowerShell: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn various methods to create new files using Windows PowerShell, from simple empty files to files with initial content, and understand the nuances of each approach.
Windows PowerShell is a powerful command-line shell and scripting language designed for system administration. One of its fundamental tasks is file manipulation, including the creation of new files. This article will guide you through different techniques to create files using PowerShell, catering to various scenarios from generating empty files to populating them with specific content.
Method 1: Creating an Empty File with New-Item
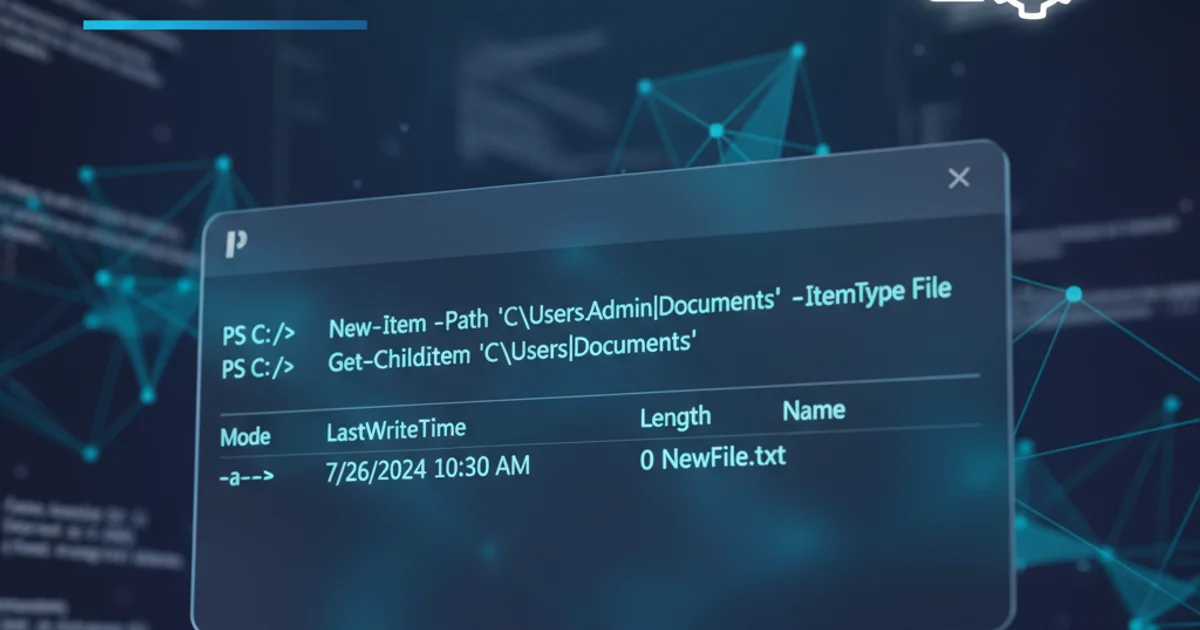
The New-Item cmdlet is the most straightforward way to create a new, empty file in PowerShell. It's versatile and can also be used to create directories. When creating a file, you specify the -ItemType parameter as File.
New-Item -Path "C:\Temp\MyNewFile.txt" -ItemType File
Creating an empty text file using New-Item
-Path does not exist, New-Item will throw an error. Ensure the parent directory exists or create it first using New-Item -Path "C:\Temp" -ItemType Directory.Method 2: Creating a File with Content using Set-Content or Add-Content
Often, you'll want to create a file and immediately write content into it. PowerShell provides Set-Content and Add-Content for this purpose. Set-Content will overwrite the file if it exists, while Add-Content will append to it. If the file does not exist, both will create it.
# Using Set-Content to create a new file with content (overwrites if exists)
"Hello, World!" | Set-Content -Path "C:\Temp\Greeting.txt"
# Using Add-Content to create a new file with content (appends if exists)
"This is a new line." | Add-Content -Path "C:\Temp\Log.txt"
"Another line." | Add-Content -Path "C:\Temp\Log.txt"
Creating and populating files with Set-Content and Add-Content
flowchart TD
A[Start] --> B{File Exists?}
B -- No --> C[Create File]
B -- Yes --> D{Using Set-Content?}
D -- Yes --> E[Overwrite Content]
D -- No --> F[Append Content]
C --> G[Write Content]
E --> G
F --> G
G --> H[End]Logic for creating/writing file content with Set-Content vs. Add-Content
Method 3: Creating a File with Redirection Operators
PowerShell also supports traditional shell redirection operators (> for Set-Content and >> for Add-Content). These are concise ways to achieve the same results as the cmdlets, especially for quick scripts or interactive use.
# Create a new file with content using > (Set-Content equivalent)
"First line of text." > "C:\Temp\RedirectedFile.log"
# Append content to an existing file using >> (Add-Content equivalent)
"Second line of text." >> "C:\Temp\RedirectedFile.log"
Using redirection operators to create and append to files
Set-Content or Add-Content cmdlets, which allow specifying the -Encoding parameter. By default, redirection often uses UTF-8 without BOM in modern PowerShell versions, but this can vary.1. Step 1: Choose Your Method
Decide whether you need an empty file (New-Item), a file with initial content that might overwrite existing data (Set-Content or >), or a file where content should be appended (Add-Content or >>).
2. Step 2: Specify the File Path
Provide the full path to the new file, including the filename and extension. Ensure the parent directory exists.
3. Step 3: Execute the Command
Run the chosen PowerShell command in your console or script. Verify the file's creation and content.