How to set null to a GUID property
Categories:
How to Set Null to a GUID Property in C#

Learn the correct and idiomatic ways to assign a null value to a GUID property in C#, including using nullable types and understanding default GUID values.
GUIDs (Globally Unique Identifiers), also known as UUIDs (Universally Unique Identifiers), are 128-bit numbers used to uniquely identify information in computer systems. In C#, the Guid struct represents a GUID. A common question arises when working with GUIDs: how do you represent the absence of a GUID, or set a GUID property to 'null'? This article explores the proper techniques for handling nullable GUIDs in C#.
Understanding GUID and Nullability
The System.Guid type in C# is a struct, which means it's a value type. Value types cannot inherently be null. When you declare a Guid variable without assigning a value, it defaults to Guid.Empty, which is a GUID consisting of all zeros (00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000). This is distinct from null.
flowchart TD
A[Guid Variable Declaration] --> B{Is it a nullable type?}
B -->|Yes| C[Guid?] --> D{Assigned value?}
D -->|Yes| E[Specific Guid Value]
D -->|No| F[null]
B -->|No| G[Guid] --> H{Assigned value?}
H -->|Yes| I[Specific Guid Value]
H -->|No| J[Guid.Empty]Decision flow for GUID variable initialization and nullability.
Using Nullable GUIDs (Guid?)
To allow a Guid property or variable to hold a null value, you must use the nullable type Guid? (shorthand for Nullable<Guid>). This allows the value type to behave like a reference type in terms of nullability, meaning it can either hold a Guid value or be null.
using System;
public class Product
{
public Guid Id { get; set; } // Cannot be null, defaults to Guid.Empty
public Guid? CategoryId { get; set; } // Can be null
public Product()
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid();
CategoryId = null; // Valid for Guid?
}
public void DisplayInfo()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Product ID: {Id}");
if (CategoryId.HasValue)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Category ID: {CategoryId.Value}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Category ID: Not assigned (null)");
}
}
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Product p1 = new Product();
p1.DisplayInfo();
Product p2 = new Product { CategoryId = Guid.NewGuid() };
p2.DisplayInfo();
Product p3 = new Product { CategoryId = Guid.Empty }; // Guid.Empty is a valid Guid value, not null
p3.DisplayInfo();
}
}
Demonstrates the use of Guid and Guid? properties.
Guid? when you intend for a GUID property to optionally not have a value. Relying on Guid.Empty to signify 'no value' can lead to confusion, as Guid.Empty is a valid GUID value itself.Distinguishing Null from Guid.Empty
It's crucial to understand the difference between a null Guid? and a Guid with the value Guid.Empty. While both might represent an 'unassigned' state in some application logic, they are fundamentally different in C#.
using System;
public class GuidComparison
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Guid? nullableGuid = null;
Guid emptyGuid = Guid.Empty;
Guid actualGuid = Guid.NewGuid();
Console.WriteLine($"nullableGuid is null: {nullableGuid == null}"); // True
Console.WriteLine($"nullableGuid has value: {nullableGuid.HasValue}"); // False
Console.WriteLine($"nullableGuid is Guid.Empty: {nullableGuid == Guid.Empty}"); // False (null is not equal to Guid.Empty)
Console.WriteLine($"\nemptyGuid is null: {emptyGuid == null}"); // False (Guid is a value type, cannot be null)
Console.WriteLine($"emptyGuid is Guid.Empty: {emptyGuid == Guid.Empty}"); // True
Console.WriteLine($"\nactualGuid is null: {actualGuid == null}"); // False
Console.WriteLine($"actualGuid is Guid.Empty: {actualGuid == Guid.Empty}"); // False
}
}
Comparing null, Guid.Empty, and a valid Guid.
null to a non-nullable Guid property, you will get a compile-time error: Cannot convert null to 'System.Guid' because it is a non-nullable value type.Practical Application: Database Interactions
When interacting with databases, especially SQL Server, uniqueidentifier columns can be nullable. Using Guid? in your C# models directly maps to these nullable database columns, simplifying data access and preventing issues with Guid.Empty being incorrectly stored as a placeholder for null.
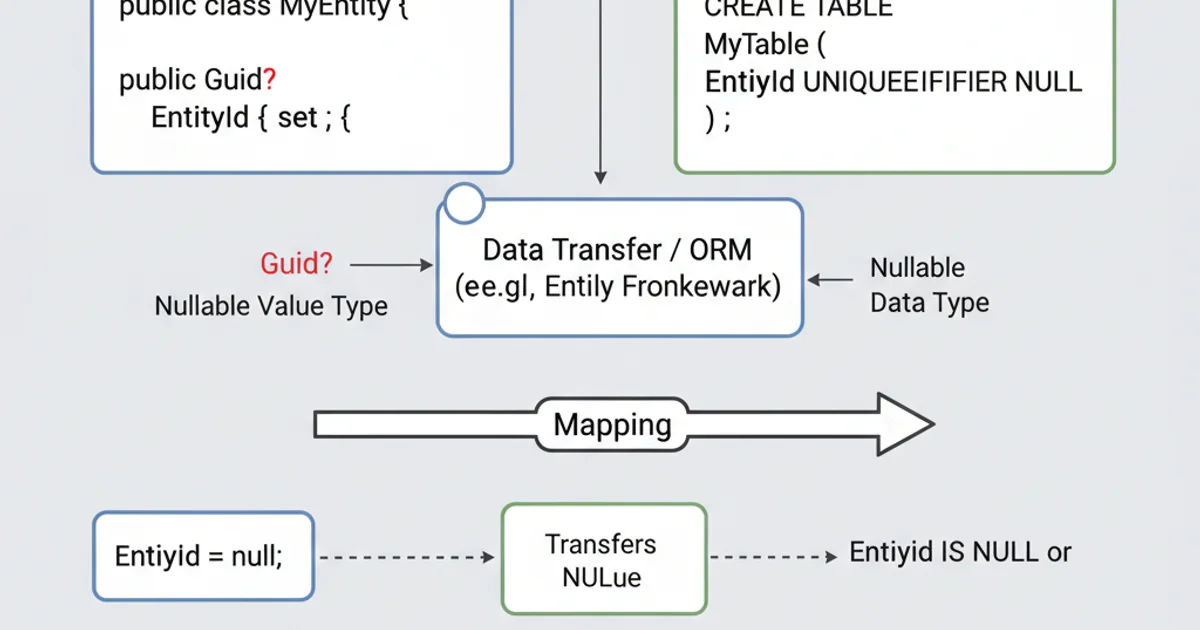
Mapping Guid? in C# to a nullable uniqueidentifier in SQL Server.