Hide scroll bar, but while still being able to scroll
Categories:
Invisible Scrollbars: How to Hide Them While Retaining Scroll Functionality

Learn various CSS techniques to hide scrollbars across different browsers (Chrome, Firefox, IE) while ensuring users can still scroll through content seamlessly.
Web design often calls for a clean, minimalist aesthetic, and visible scrollbars can sometimes detract from that. While completely removing scrolling functionality is rarely the goal, hiding the scrollbar itself while maintaining the ability to scroll is a common requirement. This article explores several CSS methods to achieve this across different browsers, ensuring a consistent user experience without sacrificing accessibility.
Understanding the Challenge
The primary challenge lies in the browser-specific implementations of scrollbar styling. There isn't a single, universal CSS property that works identically across all major browsers to hide scrollbars. Each browser engine (WebKit for Chrome/Safari, Gecko for Firefox, Trident/EdgeHTML for Internet Explorer/Edge Legacy) has its own proprietary way of handling scrollbar customization. Modern Edge (Chromium-based) largely follows WebKit's approach.
flowchart TD
A[User Wants Hidden Scrollbar] --> B{Browser Compatibility?}
B -->|WebKit (Chrome, Safari, new Edge)| C[Use ::-webkit-scrollbar]
B -->|Firefox| D[Use scrollbar-width]
B -->|IE/Edge Legacy| E[Use -ms-overflow-style]
C --> F[Set width/height to 0, background to transparent]
D --> G[Set scrollbar-width to none]
E --> H[Set -ms-overflow-style to none]
F & G & H --> I[Content Still Scrolls]
I --> J[Achieved Hidden Scrollbar]Decision flow for hiding scrollbars based on browser compatibility.
Browser-Specific Solutions
To effectively hide scrollbars while preserving scrolling, we need to apply different CSS rules for different browser engines. Below are the common approaches for WebKit-based browsers, Firefox, and Internet Explorer/Edge Legacy.
WebKit (Chrome, Safari, New Edge)
WebKit-based browsers (Chrome, Safari, and the new Chromium-based Microsoft Edge) use pseudo-elements to style scrollbars. To hide them, you can target ::-webkit-scrollbar and set its display to none or its width/height to 0.
.container::-webkit-scrollbar {
display: none; /* For Chrome, Safari, and Opera */
}
/* Alternatively, for a more subtle approach or if display: none causes issues */
.container::-webkit-scrollbar {
width: 0; /* Remove scrollbar space */
background: transparent; /* Optional: make scrollbar track transparent */
}
This method effectively removes the visual scrollbar while the content remains scrollable.
Firefox
Firefox introduced the scrollbar-width and scrollbar-color properties as part of the CSS Scrollbars Module Level 1. To hide the scrollbar in Firefox, you can set scrollbar-width to none.
.container {
scrollbar-width: none; /* For Firefox */
}
This property is specifically designed for this purpose and is the most straightforward solution for Firefox.
Internet Explorer / Edge Legacy
For older versions of Internet Explorer and the legacy (EdgeHTML-based) Microsoft Edge, the -ms-overflow-style property is used. Setting it to none will hide the scrollbar.
.container {
-ms-overflow-style: none; /* For Internet Explorer and Edge Legacy */
}
This property controls the appearance of scrollbars for elements with overflow content.
Combining Solutions for Cross-Browser Compatibility
To ensure your hidden scrollbars work across the widest range of browsers, you'll need to combine these browser-specific rules. It's best to apply them to the element that contains the scrollable content.
.scrollable-content {
overflow: auto; /* Ensures content is scrollable */
/* Hide scrollbar for IE, Edge Legacy */
-ms-overflow-style: none;
/* Hide scrollbar for Firefox */
scrollbar-width: none;
/* Hide scrollbar for Chrome, Safari, and new Edge (WebKit) */
&::-webkit-scrollbar {
display: none; /* Or width: 0; background: transparent; */
}
}
Comprehensive CSS for cross-browser hidden scrollbars.
display: none; on ::-webkit-scrollbar is common, setting width: 0; and background: transparent; can sometimes offer better compatibility or prevent minor layout shifts in specific WebKit scenarios. Choose the method that works best for your specific use case.Accessibility Considerations
Hiding scrollbars can sometimes impact accessibility, especially for users who rely on visual cues to understand content overflow or who use mouse wheels/trackpads less frequently. Ensure that there are alternative ways for users to understand that content is scrollable, such as subtle visual indicators (e.g., a fading gradient at the bottom of a scrollable area) or clear instructions if the content is critical.
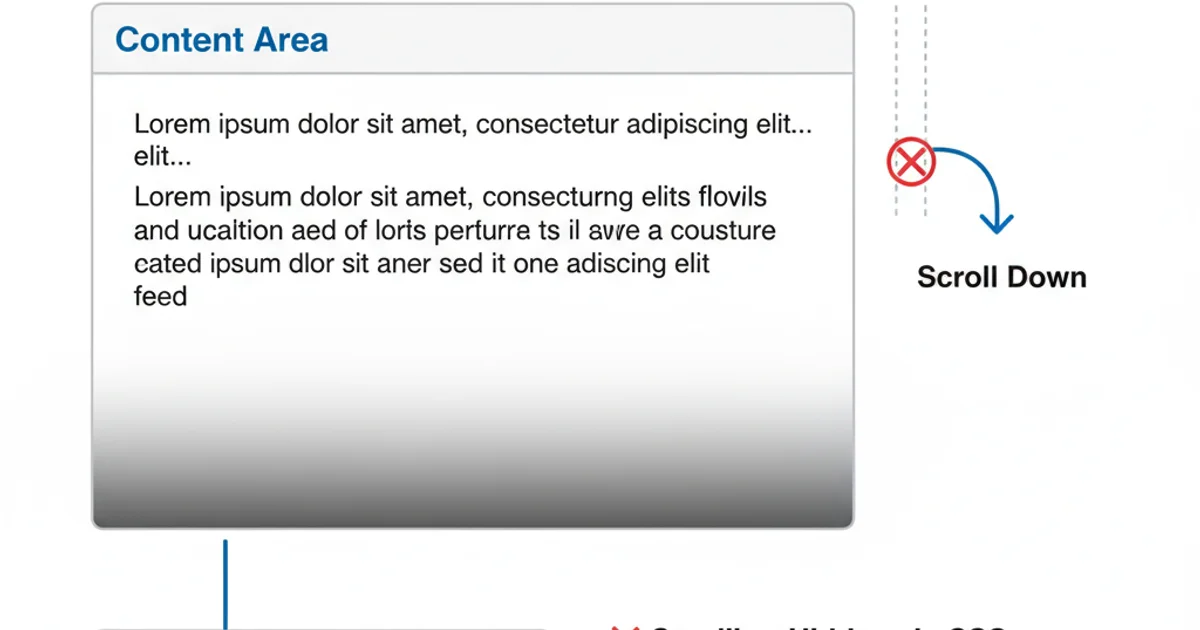
Using a subtle gradient to indicate scrollable content without a visible scrollbar.